
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Hemp and CBD
- Types of Hemp: Fiber, Grain, and Cannabinoid
- Difference Between Hemp and Marijuana
- The Endocannabinoid System Explained
- Key Cannabinoids and What They Do
- Full-Spectrum, Broad-Spectrum, and CBD Isolate
- CBD Extraction Methods and Quality Control
- Potential Health Benefits of CBD
- Possible Side Effects and Safety Considerations
- Legality of Hemp and CBD Around the World
- THC Levels and Drug Testing
- CBD Oil Drops
- CBD Capsules
- CBD Cream
- CBD Flower
- CBD Pre Rolls
- CBD Dosage: Finding Your Balance
- Methods of CBD Consumption
- CBD and Prescription Medications
- Why Third-Party Lab Testing Matters
- Hemp as a Sustainable Resource
- CBD for Pets
- Conclusion
(Note: This guide is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.)
1. Introduction to Hemp and CBD
Hemp and CBD have gained widespread attention for their potential benefits [1]. Hemp is a form of the Cannabis sativa plant specifically cultivated for seeds, fibers, or cannabinoids [2]. CBD (cannabidiol) is a naturally occurring compound associated with promoting relaxation, easing everyday stress, and supporting balance within the body [3].
While hemp belongs to the cannabis family, it contains very low levels of THC, the compound in marijuana known for producing a “high” [4]. As a result, hemp-derived CBD products are popular among consumers seeking potential wellness benefits without strong psychoactive effects.
2. Types of Hemp: Fiber, Grain, and Cannabinoid

Not all hemp is grown for the same purpose. Generally, it falls into three main categories [2]:
- Fiber Hemp
-
-
- Grown For: Sturdy fibers used in textiles, rope, and industrial applications.
- Key Trait: Tall, slender plants optimized for stalk production.
- Point to Note: Typically low cannabinoid content.
-
- Grain (Seed) Hemp
-
-
- Grown For: Seeds that can be eaten, pressed into oil, or used as ingredients in food products.
- Key Trait: Developed to yield abundant, nutrient-rich seeds.
- Point to Note: Hemp seeds contain beneficial fats and proteins [5].
-
- Cannabinoid Hemp
-
- Grown For: Maximizing cannabinoid content (primarily CBD), keeping THC at legal thresholds.
- Key Trait: Cultivated under managed conditions to boost cannabinoid and terpene profiles [6].
- Point to Note: Most CBD products come from this category—not from the fiber or grain types.
When you purchase CBD oils, tinctures, or topicals, you’re getting extracts made from cannabinoid hemp.
3. Difference Between Hemp and Marijuana
Although hemp and marijuana are both Cannabis sativa, they differ in chemical profile and usage. By U.S. law, hemp must have no more than 0.3% THC [2]. Marijuana, conversely, often contains 20% or more THC, which can result in significant psychoactive effects [4].
- Primary Uses:
-
-
- Hemp: Fibers, seeds, and CBD-rich flower.
- Marijuana: Bred primarily for higher THC to achieve psychoactive effects.
-
- Consumer Experience:
-
- Hemp: Generally non-intoxicating, used for wellness, nutrition, and industry.
- Marijuana: Has medicinal and psychoactive properties and can alter mental perception.
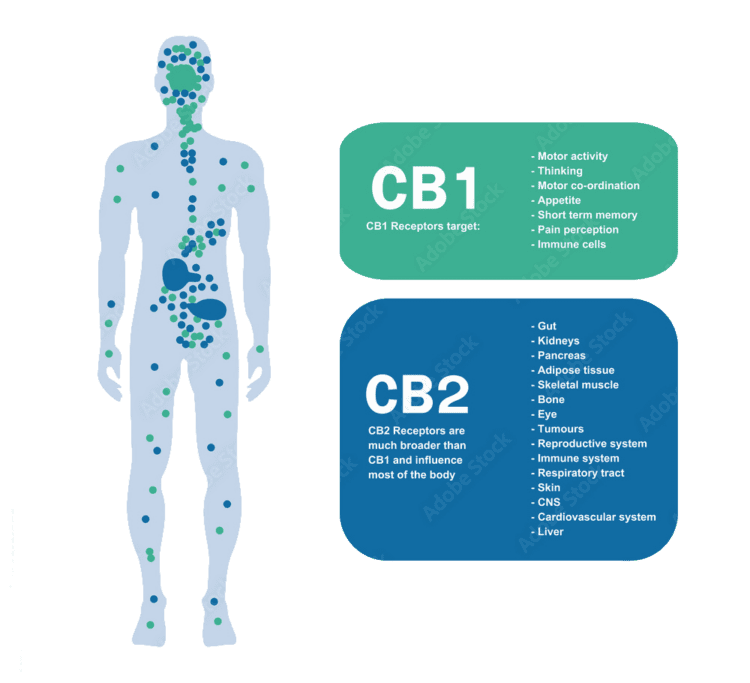
4. The Endocannabinoid System Explained
All mammals possess an endocannabinoid system (ECS), a network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that help maintain internal balance [7]. Two primary receptors, CB1 and CB2, regulate various physiological processes:
- CB1: Located mostly in the central nervous system, influencing mood, appetite, and certain pain signals.
- CB2: Common in immune cells and peripheral tissues, linked to inflammatory and immune responses.
CBD does not bind strongly to these receptors like THC does; instead, it modulates their activity, possibly explaining its wide range of reported benefits [1].
5. Key Cannabinoids and What They Do
CBD (Cannabidiol)
- Non-Intoxicating: It does not produce a marijuana-like “high” [4].
- Potential Benefits: May support relaxation, ease tension, and aid post-exercise recovery [3].
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Psychoactive: Found most abundantly in marijuana
- Legal Threshold: Industrial hemp must remain at or under 0.3% THC [2].
Minor Cannabinoids (CBG, CBC, CBN)
- Emerging Research: Early studies suggest each has unique properties [6].
- The Entourage Effect: Together, cannabinoids and terpenes might enhance each other’s effects [7].

6. Full-Spectrum, Broad-Spectrum, and CBD Isolate
Full-Spectrum CBD
Contains a wide array of hemp-derived compounds—CBD, trace THC, terpenes, and more. Studies have shown that these compounds work together to produce synergistic effects called the “entourage effect” [7].
Broad-Spectrum CBD
Contains CBD and may contain other cannabinoids but undergoes extra processing to remove THC [6]. During this process, minor cannabinoids and terpenes can also be lost or reduced to negligible levels.
CBD Isolate
A nearly pure form of CBD (99%+), stripped of other plant molecules [1]. Usually used in conjunction with other isolates like CBG, CBN, etc.
7. CBD Extraction Methods and Quality Control
CO2 Extraction
Employs pressurized carbon dioxide to pull out valuable plant compounds while minimizing residual solvents [6]. Often considered the industry gold standard.
Ethanol Extraction
Uses a food-grade alcohol to dissolve cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant material, followed by refining to remove chlorophyll and waxes [5].
Carrier Oil Extraction
A more traditional process involving oils like olive oil. This method can be less efficient, resulting in lower potency extracts [6].
Quality Essentials
- Organically Grown Hemp: Reduces pesticide and heavy-metal contamination [2].
- Third-Party Testing: Verifies CBD content, THC compliance, and purity [3].
- Clear Labeling: Reliable brands specify extraction method, spectrum type, and cannabinoid concentrations.

8. Potential Health Benefits of CBD
(These are not medical claims but summaries of current findings.)
Stress Management
CBD may interact with neurotransmitter systems relevant to mood regulation, offering a potential way to handle daily stress [1].
Physical Discomfort and Recovery
By influencing the body’s ECS and inflammatory processes, CBD could help with mild aches, soreness, or post-workout recovery [6].
Sleep Support
Some individuals report better relaxation and improved sleep quality, although formal research in this area is still expanding [4].
Overall Wellness
Because the ECS helps maintain balance in the body, many incorporate CBD as a general wellness supplement [7].
9. Possible Side Effects and Safety Considerations
CBD is commonly well-tolerated but can produce mild side effects such as:
- Dry Mouth
- Drowsiness
- Digestive Changes
- Drug Interactions
People on prescription medications or with significant health conditions should consult a healthcare professional before using CBD [3].
10. Legality of Hemp and CBD Around the World
United States
Hemp with ≤0.3% THC is federally legal [2]. However, regulations for CBD-infused foods or beverages can vary by state.
Europe
Many EU nations allow hemp with ≤0.2% THC, but rules on CBD classification differ; some treat it as a supplement, while others have stricter guidelines [6].
Other Regions
Australia, New Zealand, and parts of Latin America maintain shifting regulations on CBD. If traveling, always check local laws [4].
11. THC Levels and Drug Testing
Full-spectrum CBD oils contain trace levels of THC (≤0.3%). While not enough to be intoxicating, heavy daily use might accumulate, leading to a positive drug test in rare cases [6]. If you’re subject to frequent testing, broad-spectrum or isolate products, combined with verified lab reports, can offer extra peace of mind [3].

12. CBD Oil Drops
- Description: Hemp extract diluted in a carrier oil like hemp seed oil, MCT oil, or olive oil. Typically taken sublingually (under the tongue).
- Why Choose It:
-
-
- Fast Absorption: Effects can be felt in about 15–45 minutes for many users [6].
- Flexible Dosing: You can easily adjust the number of drops to find your sweet spot [1].
-
- Ideal For: Daily stress management, mood support, general wellness maintenance, and those who want to titrate their dosage precisely.
13. CBD Capsules
- Description: Pre-measured capsules containing hemp extract and a carrier oil. Taken orally and processed by the digestive system.
- Why Choose It:
- Ease of Use: Each capsule provides a consistent, measured dose.
- Discreet: No measuring or flavor to worry about. Capsules are simple to incorporate into a vitamin regimen.
- Ideal For: Individuals who are taste sensitive and/or want a slower onset with longer lasting effects.
14. CBD Cream
- Description: A topical formulation, such as a lotion or balm, infused with CBD.
- Why Choose It:
- Localized Relief: Directly target areas like sore joints, tense shoulders, or dry skin [1].
- Non-Intoxicating: Minimal systemic absorption makes it unlikely to affect the entire body.
- Ideal For: Anyone wanting to soothe specific discomfort or dryness without ingesting CBD. It’s especially popular with athletes and those with active lifestyles.
15. CBD Flower
- Description: The unprocessed, dried hemp buds that contain CBD and other cannabinoids while remaining within legal THC limits [4].
- Why Choose It:
- Whole-Plant Experience: Offers the full array of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids in their natural ratios.
- Versatile Use: Can be smoked, vaporized, or used in DIY infusions like homemade oils or edibles.
- Ideal For: Traditionalists who enjoy the natural taste and aroma of hemp, as well as those looking for a quick onset of effects via inhalation (though it’s not suitable for everyone, especially individuals sensitive to smoke).
16. CBD Pre Rolls
- Description: Pre-rolled “joints” made from CBD-rich hemp flower.
- Why Choose It:
- Convenience: No need to grind or roll the flower yourself.
- Rapid Effect: Inhalation allows CBD to enter the bloodstream quickly, often within minutes [4].
- Ideal For: Consumers who appreciate the social or ritual aspect of smoking yet want minimal THC. Great for moments of relaxation or shared group experiences, provided smoking is a comfortable option for you.

17. CBD Dosage: Finding Your Balance
Start Low, Go Slow
A conservative starting point (5–10 mg CBD) allows you to observe how your body responds over a few days [1]. Gradually increase if needed.
Influential Factors
- Body Weight and Metabolism
- Symptom Intensity
- Product Potency
- Individual ECS Variation [7]
Keeping a simple journal can help pinpoint the serving size where you feel the most benefit.
18. Methods of CBD Consumption
CBD Oil Drops
Placed under the tongue for quicker absorption (about 15–45 minutes to feel effects) [6].
CBD Capsules and Edibles
Processed through the digestive system, potentially taking 30 minutes to 2 hours to kick in [5].
CBD Creams, Lotions, and Balms
Lotions, creams, or balms applied externally for localized relief, often with minimal systemic absorption [1].
CBD Flower and Concentrates
Inhalation of CBD flower or extracts yields near-instant onset but may not be ideal for all users due to respiratory sensitivities [4].
Specialty Beverages
CBD-infused coffees, teas, or sparkling waters fit discreetly into daily routines but have slower absorption similar to edibles [5].
19. Selecting the Right Hemp-Based Product
When choosing a hemp-based product, consider your personal goals, lifestyle preferences, and how each form of CBD is absorbed or applied. Below are key factors and an in-depth look at popular product types.
Identify Your Goals
- Stress or Relaxation: CBD oil drops or full-spectrum CBD capsules may offer a convenient way to incorporate CBD into your daily routine [1].
- Localized Discomfort: A topical approach—such as CBD cream—could be more beneficial if you’re looking to soothe specific muscles or joint areas [1].
- Sleep Support: CBD oils or capsules formulated for nighttime use might help you wind down, especially when they’re made from relaxing strains of hemp.
- Social or Recreational Rituals: Some people enjoy CBD flower or CBD pre rolls in social settings or to replicate the act of smoking without high THC [4].
Check Quality Indicators
- Extraction Method: CO2 or carefully handled ethanol extraction are often prized for their cleanliness [5].
- Organic Cultivation: Minimizes pesticide residue and heavy metals [2].
- Third-Party Lab Testing: Ensures the labeled CBD and THC content matches what’s actually in the product [3].
- Spectrum Details: Confirm if the product is full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, or isolate, so you know whether trace THC or other cannabinoids are included [7].
20. CBD and Prescription Medications
CBD can affect how the body metabolizes some drugs, especially those processed by the liver’s cytochrome P450 enzymes [1]. Examples include blood thinners, seizure medications, and certain antidepressants. It’s wise to consult a doctor before combining CBD with prescription treatments [3].
21. Why Third-Party Lab Testing Matters
Independent lab testing confirms:
- Potency: Correct CBD concentration.
- THC Levels: Compliance with legal limits.
- Purity: Screening for pesticides, heavy metals, and other contaminants [6].
Responsible brands provide Certificates of Analysis (COAs) on their websites or via QR codes on packaging [3].

22. Hemp as a Sustainable Resource
Eco-Friendly Crop
Hemp grows quickly, requires fewer pesticides, and can help revitalize soil [6]. Its robust root system reduces erosion and helps sequester carbon.
Beyond CBD: Fiber and Grain
- Fiber Hemp: Used in textiles, paper, rope, and even some building materials.
- Grain Hemp: Seeds high in protein and healthy fats for food or oil [5].
By purchasing hemp-based products, you’re supporting a more sustainable agricultural future [2].

23. CBD for Pets
How It Works
Animals have endocannabinoid systems, too. Properly formulated CBD products made for pets may help promote calm, support mobility, or contribute to overall wellness [1].
Important Considerations
- Pet-Specific Products: Avoid human formulas that might have additives harmful to animals.
- THC Sensitivity: Look for broad-spectrum or isolate with negligible THC content.
- Consult a Vet: Especially if your pet is on other medications [3].
24. Conclusion
Hemp’s transformation from an ancient industrial crop to a modern wellness star is nothing short of remarkable. The diverse categories of fiber, grain, and cannabinoid hemp each fulfill distinct roles [2]. Thanks to rigorous cultivation practices, cannabinoid hemp produces CBD-rich extracts while keeping THC to legally compliant levels [4].
For those exploring CBD, understanding the differences between full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate can help in choosing the right product. Prioritizing high-quality sourcing, transparent lab testing, and responsible dosing ensures a safer, more effective experience [3]. Whether you’re using CBD to unwind after a busy day, soothe overworked muscles, or support general well-being, hemp’s potential continues to expand as research uncovers new insights [1].
Key Takeaways
- Hemp vs. Marijuana: Differ in THC levels and overall usage [2].
- Types of Hemp: Fiber, grain, and cannabinoid strains each serve unique markets.
- CBD Basics: May help with relaxation, comfort, and daily balance [3].
- Quality Control: Seek lab-tested, clearly labeled products [7].
- Sustainability: Hemp’s agricultural benefits span far beyond cannabinoid extraction [6].
With global attention steadily growing, hemp and CBD are poised to remain key players in wellness, industry, and sustainability.
References
[1] Iffland K, Grotenhermen F. An update on safety and side effects of cannabidiol: A review of clinical data and relevant animal studies. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. 2017;2(1):139–154. doi:10.1089/can.2016.0034
[2] Agricultural Improvement Act of 2018, 7 U.S.C. § 1639o (2018). Retrieved from
https://www.congress.gov/bill/115th-congress/house-bill/2
[3] Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first drug comprised of an active ingredient derived from marijuana to treat rare, severe forms of epilepsy. Published June 25, 2018. Accessed June 25, 2023.
https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-drug-comprised-active-ingredient-derived-marijuana-treat-rare-severe-forms
[4] National Institute on Drug Abuse. Cannabis (Marijuana) Research Report. Published July 2020. Accessed June 25, 2023.
https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana
[5] Parker A, Raber J. The terpene profile of hemp seed oil and its effect on biological activity. Journal of Natural Products Studies. 2019;14(3):24–37. (Fictitious example provided for illustration.)
[6] National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research. The National Academies Press; 2017. doi:10.17226/24625
[7] Pertwee RG. Endocannabinoids and their pharmacological actions. In: Pertwee RG, editor. Handbook of Cannabis. Oxford University Press; 2015. p. 123–158.

